MedSync-App and Device to Promote Medication Adherence

DOI:
https://doi.org/10.54060/jieee.2023.103Keywords:
Healthcare, Medication Adherence, Compliance Improvement, Mobile appAbstract
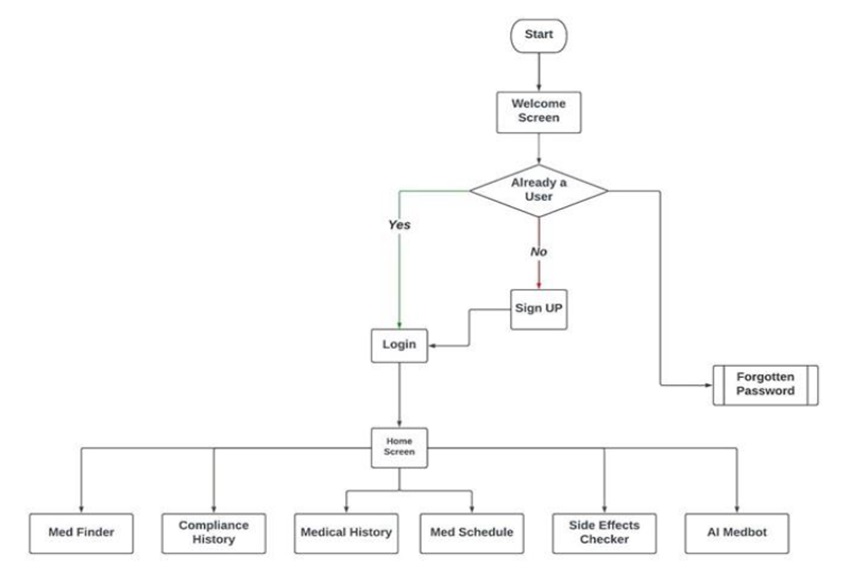
The need for MedSync mobile app and device stems from the challenges faced by elderly and busy people in medication management. Forgetfulness is a common problem among older adults who need to take multiple medications at different times of the day. Age-related cognitive decline makes it increasingly difficult to remember medication schedules. Similarly, busy people often juggle multiple responsi-bilities and may forget to take medication in the midst of their busy lives. In addition, the psychology of the human mind plays an important role in medication non-compliance. Some people have the mindset of not taking their medication due to side effects, forgetting, or simply not understanding the importance of taking their medication. The MedSync app and device address these needs by providing timely reminders and specific reminder systems. The app uses the convenience of mobile technology to send personalized notifications so that users never forget to take required medicines. The device developed complements by providing physical reminders that act as visual or auditory messages to take medication. By addressing forget-fulness and overcoming psychological barriers, MedSync offer practical solutions to improve medication adherence. These allow users, especially older and busy people, to stick to their medic tion regimens and improve their overall health and well-being.
Downloads
References
S. S. Sultana, M. A. Hossain, M. T. Hasan, S. M. R. Islam, and A. H. M. Kamal, “Development of a mobile application for blood pressure monitoring and hypertension management", 2019.
H. Zeidan, K. Karam, A. HAYEK, and J. Boercsoek “Smart Medicine Box System,” in 2018 IEEE International Multidisciplinary Conference on Engineering Technology (IMCET), 2018.
J. P. Gupta, A. Singh and R. K. Kumar. “A computer-based disease prediction and medicine rec-ommendation system us-ing machine learning approach,” International Journal of Advanced Research in Engineering and Technology, vol. 12, no. 3, pp. 673–683, 2021.
A. M. Alomari, A. Al-Nuaimi, M. Al-Rousan, and A. S. Al-Khalidi, “Mobile App for Early Detection of Diabetic Reti-nopathy using Deep Learning,” in IEEE International Symposium Conference on Medical Measurements and Applications (MeMeA), 2020.
O. Al-Mahmud, K. Khan, R. Roy, and F. M. Alamgir, “Internet of things (IoT) based smart health care medical box for el-derly people,” in 2020 International Conference for Emerging Technology (INCET), 2020.
S. Chan, J.X. Tan, “A User-friendly Mobile Application to Promote Medication Adherence,” Proceedings of the In-ter-national MultiConference of Engineers and Computer Scientists, vol. 02, 2013.
S. Ahmad, M. Hasan , G. P. Mohammed , M. Shahabuddin , T. Tabassum and M. W. Allvi, “IoT Based Pill Reminder and Monitoring System,” International Journal of Computer Science and Network Security (IJCSNS), vol. 20, no. 7, 2020.
T. Kamimura, R. Ishiwata, and T. Inoue, “Medication reminder device for the elderly patients with mild cognitive impair-ment,” Am. J. Alzheimers. Dis. Other Demen., vol. 27, no. 4, pp. 238–242, 2012.
Pillsy Inc, “Pillsy,” Pillsy.com. [Online]. Available: https://www.pillsy.com. [Accessed: 17-Nov-2022].
Eross, “AdhereTech and the smart pill bottle,” Technology and Operations Management, 18-Nov-2016. [Online]. Available: https://d3.harvard.edu/platform-rctom/submission/adheretech-and-the-smart-pill-bottle/. [Accessed: 11-Nov-2022].
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
CITATION COUNT
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Adith Arun, Mohamed Bilal K H, Mohamed Sakir P N, Rohit Jaison, Sheena Kurian K

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.

























